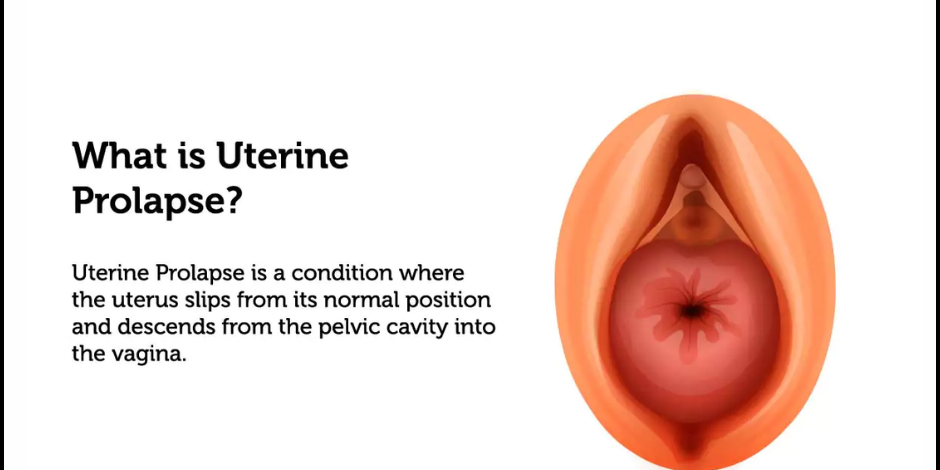
Uterine Prolapse is a condition where the uterus slips from its normal position and descends from the pelvic cavity into the vagina. The degree of prolapse can range from mild to severe, depending on how far down the uterus has descended. It is more common in postmenopausal women who have had multiple vaginal deliveries because childbirth stretches and weakens these muscles.
Types of Uterine Prolapse
- There are four types of Uterine Prolapse: cystocele, rectocele, enterocele and uterine descent.
- Cystocele: It is characterized by the bulging of our bladder into your vagina. It happens when your vaginal wall weakens and as a result, your bladder drops from its normal location.
- Rectocele: It occurs when the muscular walls that separate the rectum from your vagina weaken or stretch, allowing part of your rectum to bulge through your vaginal wall.
- Enterocele: It is typically caused by repeated straining due to constipation, childbirth or the aging process. The descending parts of the intestines may press on one side of the cervix and force it against its surrounding support tissues, causing them to stretch downwards towards our lower abdomen before they start to protrude out of our vagina as an internal ballottement defect, which we call an enterocele
- Uterine Descent: It is diagnosed if any uterine consistency drops down towards our vaginal opening without causing any bladder or bowel defects that cause changes in our pelvic floor muscles or contents like those seen with cystoceles, rectoceles or enteroceles.
What causes uterine prolapse?
- Uterine prolapse is caused by a weakening of the pelvic floor muscles and supporting ligaments, which can be due to childbirth, menopause, chronic constipation, or straining due to coughing.
- Other risk factors include being overweight, having a history of hysterectomy or pelvic surgery, and fractures of the pelvis.
What are the symptoms of Uterine Prolapse?
- Stress incontinence – Accidentally leaking urine when coughing, sneezing, laughing or exercising.
- Pelvic pressure or a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Low back discomfort
- Sensation of pulling in the groin area.
- Difficulty in having a bowel movement or urinating.
- Feeling of something pressing against the vaginal opening.
- Trouble comfortably wearing tampons.